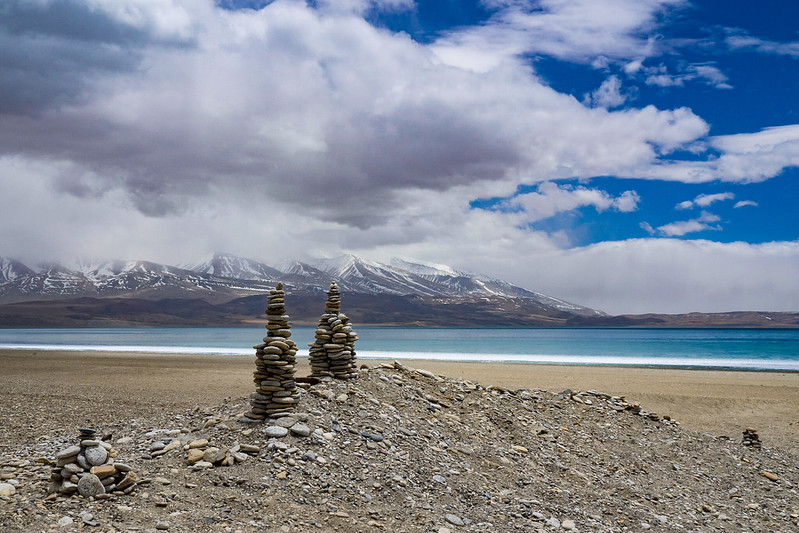
Source: Flickr_Manasarovar Lake _ Manasarovar Lake – Tibetan Plateau – Tibe…
Introduction
The Tibetan Plateau, which is many times referred to as the “Roof of the World,” is a much more important feature than being purely geographical. In the light of the huge frozen water reservoir it forms, it plays an important part in the global climate system. The uniqueness of this region has acquired for itself the title “Third Pole,” referring to its enormous importance. Here, we are going to bring out the geological formation, climatic condition, and ecological importance of the Tibetan Plateau. We will also find out the challenges emanating from climate change and the need for protection that this crucial water tower of Asia needs.
Geological Formation of Tibetan Plateau
It is a consequence of the gigantic geological event that resulted in a collision-the India-Eurasia collision-between the two great landmasses. Over millions of years, the Indian subcontinent, a big chunk of land, had been drifting northward until it finally collided with the Eurasian Plate. Concomitant with the tectonic crunch, the Earth’s crust was thrown upwards to crumple and fold this gigantic mountain range of the Himalayas and a great expansive highland area called the Tibetan Plateau.
The tectonic forces working in this region shape this land continuously. Earthquakes and other geological events are common, showing the, in fact, really dynamic nature of this land mass: the Tibetan Plateau. These ongoing processes contribute to varied relief on the plateau, such as towering peaks, deep valleys, and vast glaciers.
Climatic Conditions of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau has an extreme and harsh climate. Because of the high altitude, it faces bright solar radiation. There is great fluctuation in the range of temperature both during summer and winter seasons. During the daytime, the temperatures can remain scorching; however, during nightfall, temperatures may even become bitterly cold. Strong winds prevailing on the plateau create tough conditions for humans and wildlife.
Despite the extreme climate condition of the area, the Tibetan Plateau has an unusually big, broad influence on the world’s weather. Due to its height and geographical position, it has an impact on atmospheric circulation, and thereby affects the precipitation pattern and temperature distribution of greater parts of Asia. The Tibetan Plateau acts as a natural conditioner of air; due to its cooling effects, neighboring areas, along with monsoon patterns, are influenced.
Ecological Importance of Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau comprises a well-identified biodiversity hotspot with a wide array of unique plant and animal species. Its various ecosystems provide a range from alpine meadows to high-altitude deserts. Many of these ecosystems are fragile and vulnerable to environmental disturbances.
One of the most overwhelming ecological aspects of the Tibetan Plateau is, in fact, its vast store of glaciers, holding copious amounts of freshwater that play an extremely important role in sourcing a number of major rivers in Asia: the Yangtze, Yellow, Indus, Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Mekong. These rivers support billions of people, providing water for agriculture, drinking, and hydropower generation.
The Threat of Climate Change
The Tibetan Plateau faces imminent danger due to the emerging threat of climate change. This rising temperature is leading to a tremendous rate of glacier melting, which in turn is leading to a drop in the water availability. This may result in very extreme downstream consequences, particularly considering that the dry seasons are approaching. In addition, other contributing factors to the extreme weather include increased frequency and intensity of droughts, floods, and landslides, which seriously added to the regional challenges.
This, in turn, also causes sea-level rise and thus threatens the coastal communities of different parts of the world. Glaciers on the Tibetan Plateau make one of the most extensive contributions toward global sea-level rise, and further losses might have large-scale consequences.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Development
The Tibetan Plateau deserves protection as a livelihood for billions of people. Therefore, conservation is in full swing by tending to the challenges brought forth by climate change and ensuring the sustainable use of the natural resources found in the region. The following are some of these actions:
- Glacier Monitoring: Scientists monitor the rate of retreat of glaciers to fully understand the impacts of climate change and develop ways through which to conserve the region.
- Sustainable land use: In using sustainable agriculture and forestry practices, there will be an easy way of protecting the ecosystems of the plateau and offering protection against erosion and deforestation.
- Renewable energy: Various renewable sources of energy such as solar and wind power could be invested in as a way of relying less on the fossil fuel sources in the region, hence mitigating the impacts of climate change.
- International cooperation: The government must take effective steps to encourage international cooperation among the nations sharing the Tibetan Plateau, in view of implementing effective conservation and sustainable development.
The Role of the Tibetan Plateau in Global Climate Patterns
Beyond its regional significance, the Tibetan Plateau has a very important position in global climate patterns. The height and geographical position of the plateau have joined to make it a natural dam that affects atmospheric circulation and precipitation across Asia. Its height causes the climate to be cold and dry at most times, even inducing high-pressure systems at times. Such high-pressure systems might influence the course of monsoon winds and their intensity, further affecting rainfall in regions like South Asia and Southeast Asia.
This plateau also serves as the most significant impetus to the development of the Asian monsoon, a seasonal wind system responsible for heavy rainfall in much of Asia. The topography and temperature gradients surrounding the plateau influence the start and intensity of the monsoon and, therefore, impact agricultural productivity and water supply within the region.
The Tibetan Plateau and Biodiversity
In spite of the severe climate of the plateau, there is great diversity among the plant and animal species in the Tibetan Plateau. There have been many species habits and specialized adaptations that have occurred due to the unique ecological features of this area. Examples include, but are not limited to, the rare and endangered species-like Tibetan antelope and snow leopard.
Then again, good ecosystem health and resilience also rely on the biodiversity of the Tibetan Plateau. Forests, grasslands, and wetlands are some of the most crucial ecosystems when it comes to the regulation of water flow, prevention of soil erosion, and maintenance of species habitat. In protecting this biodiversity on the plateau, one would actually be ensuring long-term sustainability in its ecosystems.
Sustainable Development Challenges on the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau still faces many challenges on the road to sustainable development: the fragile ecosystem has been seriously damaged by overgrazing, deforestation, and mining methods. It causes soil erosion, destruction of habitats, and changes in climatic conditions.
Moreover, a remote location and even the hostile climate of the plateau impede carrying out projects of sustainable development. The construction of infrastructure, roads, and power plants brings negative impacts on the environment. The challenge in striking a balance between economic development and nature protection calls upon the plateau.
The Significance of International Level Cooperation
The Tibetan Plateau is a heritage shared by all humankind, for which its protection and sustainable development require international cooperation. Parts of it fall within China, India, Nepal, Bhutan, and Pakistan. Any efforts toward effective conservation and development must, therefore, be coordinated among these countries if they are to address their common challenges and accrue maximum benefits from this treasure.
This also opens a path toward international collaboration in knowledge and resource sharing. Collaboration will enable countries to work jointly on research projects, sustainable development, and concerns on the environment that cross boundaries.
Future of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau is shrouded in uncertainty regarding its future, but the challenges it faces are crystal clear. From climate change to human activities in need of sustainable development, a lot of the issues need consideration. In order to work toward a sustainable future in this vital region, one can try building a conceptual framework by taking a holistic approach that considers the ecological, social, and economic dimensions of the plateau.
The Tibetan Plateau is a unique and irretrievable resource that has played an important role in global climate patterns and biodiversity. Protecting this area, however, requires international cooperation, sustainable development practices, and a commitment to conservation. By working together, we can ensure the Tibetan Plateau continues as a thriving and resilient ecosystem into the future.
Sources:
- https://earthsky.org/earth/earths-3rd-pole-aka-the-asian-water-tower-is-melting/#:~:text=Earth’s%203rd%20Pole%2C%20aka%20the,to%2025%25%20of%20Earth’s%20population.
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s43017-022-00299-4
- https://dialogue.earth/en/water/review-governing-the-water-tower-of-asia/
- https://www.unep.org/events/unep-event/launch-event-scientific-assessment-third-pole-environment