Source: Wikimedia_Socotra_socotra-galapagos-biodiversity-indian-ocean
Introduction
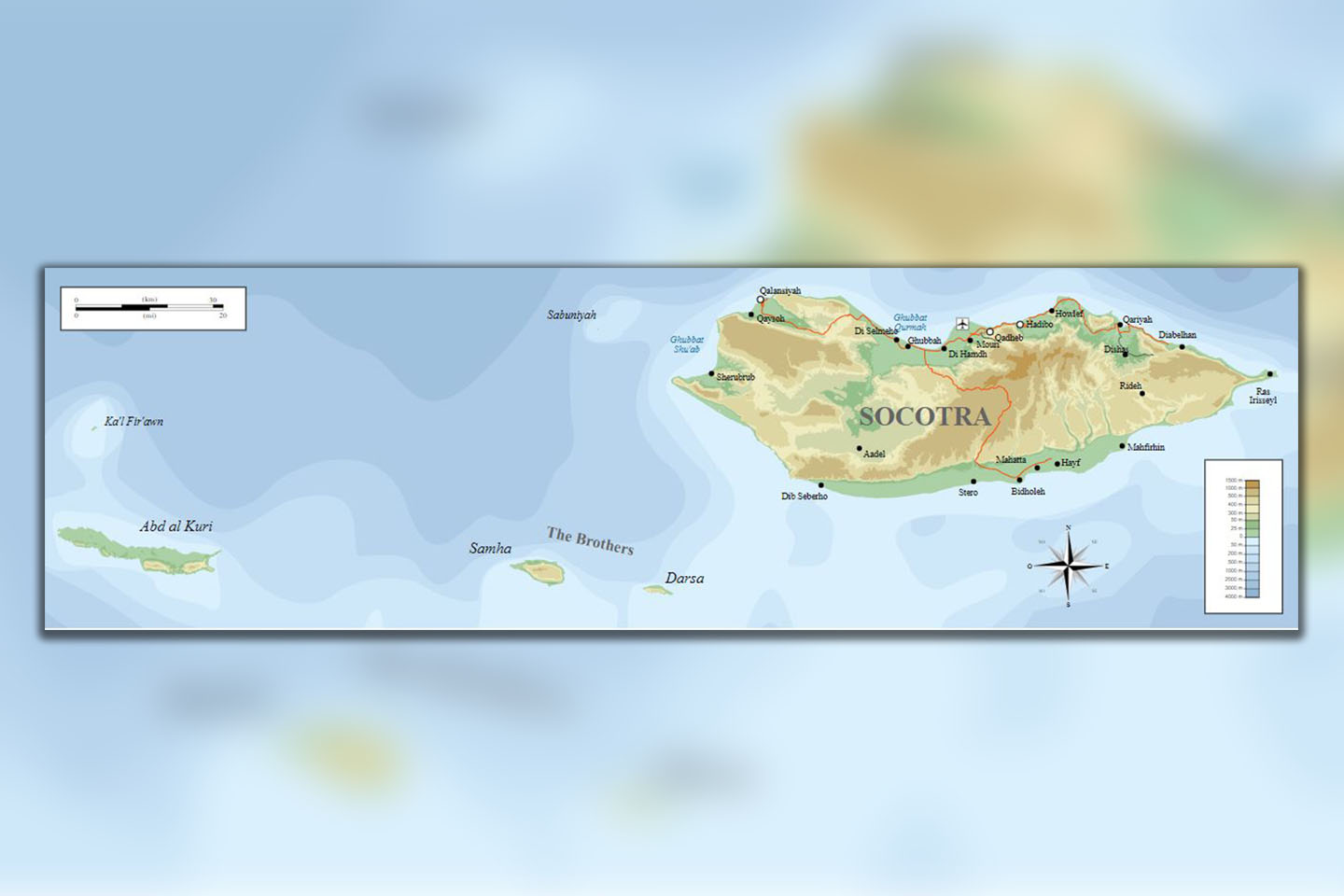
Socotra: An archipelago belonging to Yemen, cradled in the Arabian Sea. It is called a biological treasure and often the “Galapagos of the Indian Ocean”. It is believed that the isolation and a unique set of environmental conditions conspired for the evolution and adaptation where a flora-fauna ensemble found in many endemics gave testimony to the wonders of nature. And for the record, its set-up and geological past uniquely created an ecosystem that does not exist anywhere on Earth.
A Geological Tapestry
Geology on Socotra is almost as diverse as its biodiversity. The archipelago is located right at the crossroads of Africa, Asia, and the Indian Ocean, emerged from the depopulation millions of years ago. The isolation and harsh conditions caused by desert climate nurtured the development of extraordinary forms of biodiversity, which adapted to these conditions.
Its variegated topography lends support to a varied host of habitats such as rugged mountains, sandy plains, and clean beaches. Populating these varied niches is found a huge diversity of plant life, from the towering Dragon Blood Trees to the elusive Socotra chameleon.
A Botanical Wonder

Source: Wikimedia_Dragon’s_blood_trees,_Diksam_plateau,_Socotra_Island
The flora of Socotra is simply mind-blowing. One-third of the plant species in this island are not to be found anywhere in the world. Its most iconic plant, the Dragon Blood Tree, is a living testimony to this extraordinary biodiversity. This tree has for centuries fascinated explorers and botanists with its umbrella-shaped canopy and crimson red resin.
After the Dragon Blood Tree, Socotra also has one of the most diverse varieties of flora, which includes the desert rose, frankincense trees, and succulents that have evolved to live in such arid conditions. The flora of the island is an epic of adaptability, where they develop features to protect themselves against water shortage, breeze, and extremely poor soils.
Zoological Marvels

Source: Wikimedia_Dragon’s_blood_trees,_Diksam_plateau,_Socotra_Island
The animal kingdom is equally amazing, with high endemism in reptiles, birds, and invertebrates. Among the island’s reptiles, for example, the Socotra chameleon has developed its own particularities to go unnoticed and capture its prey in the very hostile environment of the desert.
Being so unique, the Socotra island hosts great diversity in birdlife, harboring endemic species such as a starling, Socotra sunbird, and Socotra bunting. Isolation has caused the birds to evolve special features of this habitat, reflected in their diet and breeding pattern.
Invertebrates, and especially butterflies and spiders, are the most endemic species of Socotra. Through its unique ecological conditions, the island holds a very great number of insect species crucial for the pollination of the island’s flora.
The Fragile Ecosystem
Although biodiversity on Socotra reaches high levels, its ecosystem itself is fragile and under many threats. Climate change, overgrazing, deforestation, and invasive species put at risk the unique flora and fauna on the island.
The conservation of the natural heritage of Socotra is supported by the collective human efforts. The island has been a UNESCO World Heritage since 2008 because of its outstanding universal value. Conservation organizations and local communities have been at the forefront in pushing for policy-making on sustainable practices, thus fueling the awareness of Socotra’s biodiversity.
The Unyielding Soul of Socotra: A Struggle for Survival
Human isolation made Socotra a crucible for the creation of singular biodiversity. Turned now by isolation into a double-edged sword, while it has harbored a world apart, it has left its inhabitants particularly at risk. The fine ecological balance of the island, polished over millennia, now is challenged from a confluence of human-created pressures.
The Challenge of Climate
In fact, climate change is not anybody’s friend and casts a long shadow over Socotra, so perfectly fine in all other ways—its globally strong ecosystem of flora and fauna notwithstanding. Global warming and changed precipitation have deleterious effects on the island’s delicate ecological rhythms. A large number of endemic species, with very delicate adaptations to certain climatic conditions, could not respond. Consider the Dragon Blood Tree, symbolizing Socotra—showing signs of stress due to altered precipitation regimes. Another eminent challenge is the rise in sea level that threatens to inundate the coastal habitat and displace the flora and fauna.
Invasive Species: Silent Invaders
A further critical challenge is the entry of non-native species, often due to accidental release by human activities. The introduced plants and animals have drastically caused a decline in the numbers of native species and, in some instances, extinction. Goats introduced for producing meat and milk have caused overgrazing that spans to large areas and results in soil erosion and loss of vegetation. Conversely, plant species such as the prosopis juliflora, invasive and commonly referred to as the mesquite tree, has been invading native habitats at a rapid rate.
Unsustainable Practices and Overexploitation
Such human activities as overfishing, deforestation, and unsustainable land use, increasingly add up to overstretch the ecosystems of Socotra. Due to overfishing, fish populations have drastically been reduced thus tampering with marine biodiversity and compromising the capacity of coastal fishing to support livelihoods. Deforestation, particularly for fuel wood and construction materials, causes habitat loss and leads to soil erosion.
Conservation Efforts: The Silver Lining
Fully cognizant of the situation, an international, national and local coalition is at work protecting the unique heritage of Socotra. UNESCO’s status as a World Heritage Site brings world attention to the island that enables conservation efforts.
Conservation puts the local people into a responsible role of stewardship towards the environment. The community-based programs center on sustainable livelihoods, education, and awareness. Through the involvement of the local population, environmental conservation becomes more effective and much more likely to endure.
Socotra is also a hub for understanding its ecosystems and coming up with strategies that will facilitate proper conservation. Biodiversity, climate patterns, and effects of human activity on the island are the subject of research aimed at informing future conservation planning.
A Sustainable Future for Socotra
To save Socotra, there is a need for the implementation of sustainable development that takes into consideration both the conservation of the local people’s livelihoods and the island’s natural heritage.
Energy sources that are renewable in nature will cut down the dependency on fossil sources, thereby reducing the amount of environmental change. Ecotourism is a way of creating revenues without serious environmental degradation. Proper approaches to agriculture and fishery can provide food security while maintaining biodiversity in an area.
In the end, the future of Socotra belongs to its people and the larger society. Together, we are able to make a difference and preserve this most remarkable island for future generations. Socotra’s natural endowment is a treasure beyond price and merits protection above all levels.
Sources:
- https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1263/#:~:text=Socotra%20is%20of%20particular%20importance,Gal%C3%A1pagos%20of%20the%20Indian%20Ocean%E2%80%9D.
- https://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/conservation/issues/socotra-yemen.htm
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-middle-east-44235159
- https://www.cntraveller.com/article/socotra