Source: Wikimedia_Mohenjo-daro_By Saqib Qayyum
When you talk to your grandparents or anyone old in general, do you ever think about how different their life must have been? The age gap might not be much but the generation gap does wonders to the distinction between the life we have lived and the one lived by our seniors. This thought is what drives our historians and archaeologists to work and research about what happened in the past.
The scriptures and artifacts left by the ancient ones are studied to understand the way civilizations developed and ultimately, perished. Many scripts have been found and deciphered. Deciphering these codes enhances our understanding about the ancient civilizations that used them.
One such civilization is the Indus Valley civilization whose discovery was groundbreaking. We found numerous records, tablets, and ruins which were studied intensively. But even after intense research, we still haven’t cracked the Indus code. What seems to be the problem?
How do scripts get deciphered?
Let us first understand how ancient scripts are cracked. We will use the example of the Rosetta Stone for this purpose. The Rosetta Stone was found by the French in 1799 who found that it dated back to 196 BC. The stone had been carved by the Egyptians and the carvings had been written down in three different ancient scripts. The first was the hieroglyphic script of the Egyptians. The third was ancient Greek. And the second one- the one in the middle- was the demotic script which is a cursive form of ancient Egyptian similar to written Arabic.
The three different scripts were a boon for researchers. Many people who were working on this stone knew how to read and decipher Ancient Greek. What they did was genius- they cracked the meaning of the Ancient Greek carvings and compared the meaning with the hieroglyphic script. This helped them recognize repetitive symbols and then, crack the Rosetta code. No one would have seen this coming 200 years ago. But we had found such an important artifact and successfully cracked the code.
With the recent developments in technology, many researchers are now also using machine learning and translations to understand more ancient scripts. Other than the Indus code, researchers are also trying to translate 69,000 Mesopotamian records. This is going to be done by using machine translation. The project is ongoing and its success will pave way for future projects.
Discoveries of Indus
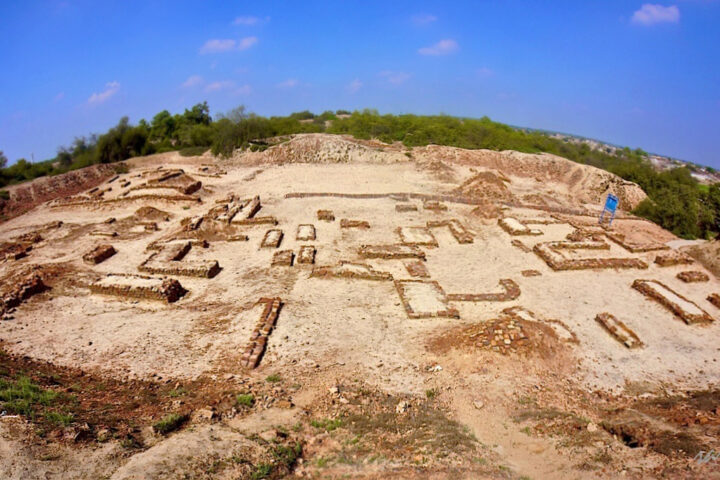
The ruins of the Indus Valley civilization were found in parts of present-day Pakistan and Punjab. There are two main cities in this civilization – Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro. Harappa is situated on the left bank of the Ravi River. Slightly smaller than Mohenjo-Daro, it stands on a mound upon which a citadel was built on the west, and workers’ quarters on the east. This was but one part of the city and the archaeologists also found granaries, administrative sections, barracks, and a podium.
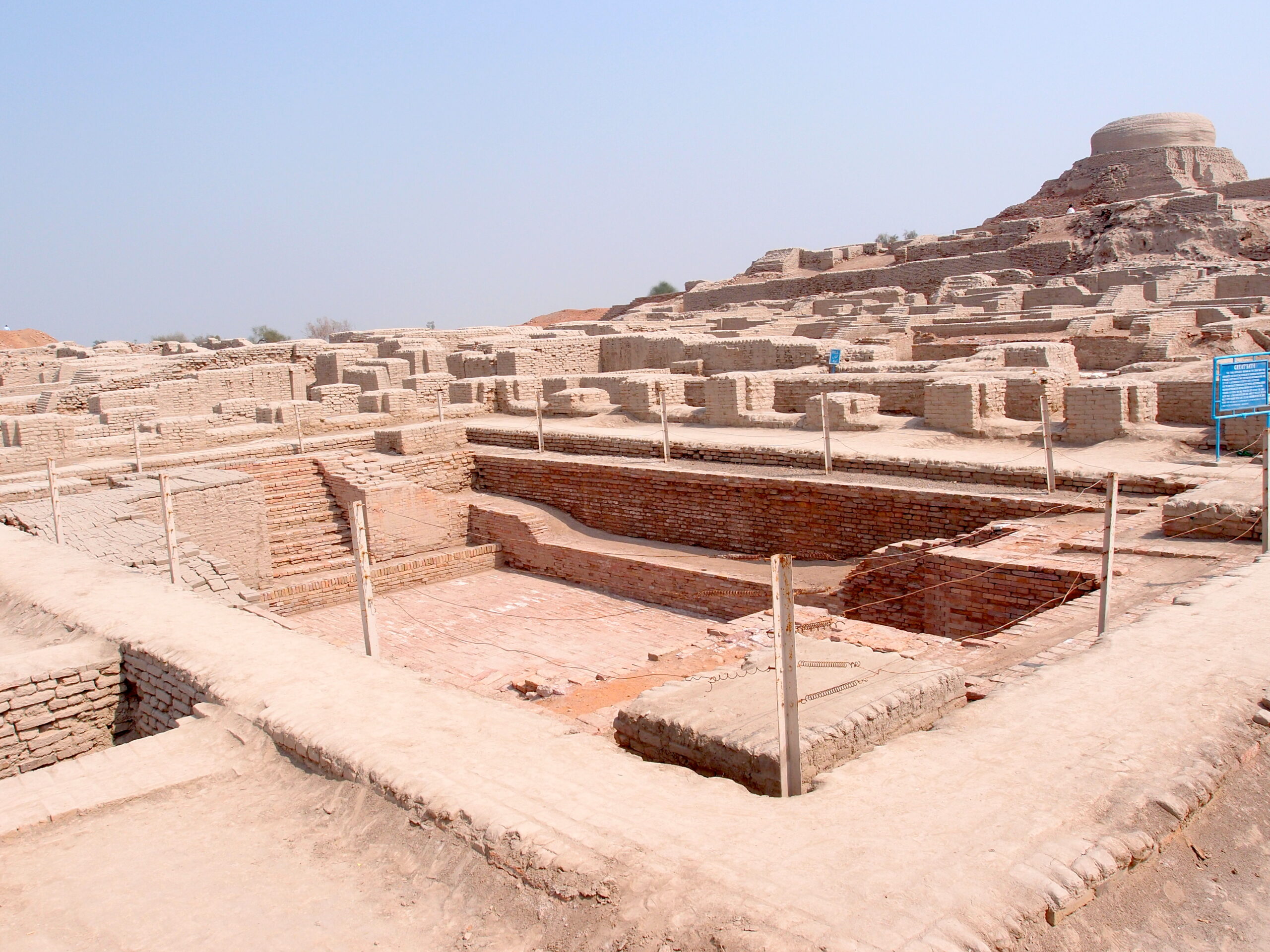
On the right bank of the river lies Mohenjo-Daro. This city was situated on the flat Indus plains. The name of the city literally translates to ‘the mound of the dead’, and has immense historical importance. Designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980, the city has a lot of monuments which, in turn, hold tons of rich artifacts.
The findings show us that these guys were very progressive and had an administrative and irrigation system. They knew how to grow a variety of crops like barley, cotton, peas, mustard, and sesame and how to domesticate animals like dogs, cats, pigs, buffaloes, and cattle. They also had a political system, extensive trade system, weights and measures and specialized in crafts production, import, and export. And between all this is the Indus script with all its mystery. What we have found is already so impressive, what will happen when we actually understand the code for all of this?
Why don’t we know yet?
In the example we noticed above, we discussed how a known script in the Rosetta stone was used to decipher the unknown script. In the case of the Indus script, we don’t have anything like that. The lack of a proper reference for this ancient script has made it very difficult for scholars to crack it. Add to this the fact that this script is a collection of symbols whose relative frequency doesn’t really tell anything about the script. Over 100 attempts have been made to understand the signs and runes left by the Indus people but none of these were unsuccessful.
Many researchers tried to compare it to the Cuneiform script of Mesopotamia and study similarities between the two. The inability to translate this script was so frustrating that in 2004, one group of scholars declared that the Indus people were functionally illiterate. This was rejected by a team of mathematicians and computer scientists recently who used computer modeling to show that the script communicated language for sure.
This was one step towards using technology to understand the script. But we have a long way to go. The process of analysis and translation will take many more years. The end result would be fantastic though. We would understand about the script, the administrative system, and hopefully, also about the disappearance of this civilization.
Resources
- Pare, S., & LiveScience. (2023, July 19). Ancient “Unknown” Script Is Finally Deciphered. Scientific American; Scientific American. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/ancient-unknown-script-is-finally-deciphered/
How do scripts get deciphered?
- Plackett, B. (2022). How Do Archaeologists Crack the Code of Ancient Languages? Discover Magazine; Discover Magazine. https://www.discovermagazine.com/planet-earth/how-do-archaeologists-crack-the-code-of-dead-languages
- Hardach, S. (2018, December 10). The key to cracking long-dead languages? Bbc.com; BBC. https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20181207-how-ai-could-help-us-with-ancient-languages-like-sumerian
Discoveries of Indus
- Ravi River | Map, Origin, Development, & Location | Britannica. (2024). In Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Ravi-River
- Mohenjo-daro | Artifacts, Definition, Map, & Facts | Britannica. (2024). In Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Mohenjo-daro
- Indus civilization – Craft, Technology, Artifacts | Britannica. (2024). In Encyclopædia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/topic/Indus-civilization/Craft-technology-and-artifacts
Why don’t we know yet?
- Roychowdhury, A. (2024, January 8). The mystery of the Indus script: Dravidian, Sanskrit or not a language at all? The Indian Express; The Indian Express. https://indianexpress.com/article/research/the-mystery-of-the-indus-script-dravidian-sanskrit-or-not-a-language-at-all-9099880/
- Lawler, A. (2004). The Indus Script–Write or Wrong?.
- admin. (2014, April 29). Decoding the Ancient Script of the Indus Valley. Archaeology Online. https://www.archaeologyonline.net/artifacts/indus-valley-script