Source: Wikimedia_By Stewart Butterfield – Flickr Valentines Chocolates, CC BY 2.0
Introduction
Chocolate is one such delicacy enjoyed by millions around the world. It has an interesting history that is weaved together for thousands of years, from being a medicinal drink to the Americas to becoming a sought-after confectionery product worldwide. It is a story of cultural exchange, culinary innovation, and economic impact.
Pre-Columbian Chocolate: A Sacred Beverage
The origins of chocolate date back to Mesoamerica, where this prized foodstuff has been nurtured with a smile by the forefathers of the ancient Olmec, Maya, and Aztec civilizations. The former believed that chocolate held divine properties and used it in religious ceremonies and as a symbol of status.
Chocolate was typically a frothy beverage ready for drinking by grinding out cacao beans to make paste, mixing with water, and adding spices such as chili peppers, vanilla, or honey. This frothy drink, known to the Aztecs as “xocolatl,” was, in fact, believed to provide energy and vitality.
Spanish Conquest and Introduction to Europe
Upon entering the Aztec Empire in 1519, Hernán Cortés, a Spanish conquistador, discovered chocolate. Bothered by its peculiar flavor and medical properties, cacao beans were taken from the Aztecs by Cortés to Spain.
Initially, chocolate was considered to be of questionable taste in Europe since its bitter taste and unusual texture were unfathomable to the Europeans. However, for Spanish royalty and nobility, the origin of this product was exotic, and they started experimenting with ways of preparing it.
European Innovations and Improvements
While this led to a boom in chocolate production in the New World, over time, Europeans also developed a preference of their own for chocolate-a more refined preparation process and the addition of ingredients to make it palatable. They experimented with various sweeteners, such as sugar and honey, and flavors like cinnamon, nutmeg, and almonds.
Adding sugar was the turning point, which transformed chocolate from a bitter beverage to that delicacy; every time that sugar was commonly accessed, chocolate just skyrocketed more among the elite of Europe.
Chocolate of the 17th and 18th Centuries
Chocolate demand remained on a steady increase throughout the 17th and 18th century in Europe. Chocolate houses, establishments were instituted for people to socialize and drink hot chocolate along with other social functions.
With it came more industrialized production of chocolate. Chocolate makers began innovating new ways to roast, grind, and mold cacao beans, making its availability even more widespread among greater percentages of the population.
Chocolate in the 19th Century: A Global Sensation
The 19th century marked a turning point in the history of chocolate. Industrialization brought about technological innovations that led to mass production of this sweet candy. It became even more pronounced with increased global trade as chocolate began to thrive around the world.
In the United States, chocolate became a favorite of confectionery products, and again Hershey’s, Mars, among others, introduced such exciting candies like chocolate bars. These innovations also made chocolate more accessible and cheap in an effort to make it even popular.
Chocolate in the 20th and 21st Centuries: A Global Craze
The last two centuries have thus seen an explosion in the popularity of chocolate. Among the new tastes, flavors, and textures, there could be as much emphasis on doing justice to the diverse tastes and preferences.
Dark chocolate has quickly gained wide acceptance. Dark chocolate has a higher percentage of cocoa solids and antioxidants. Fair trade chocolate is also gaining momentum because of its support for the cause of sustainable farming practices and good labor standards among health-conscious consumers.
Today, its delight is enjoyed by mankind from the busy streets of Tokyo to the quiet villages of Africa. Its enduring popularity can be attributed to its rich history, complex flavors, and cultural significance.
Economic Impact of Chocolate
The chocolate industry has accounted for much of the revenues of many nations. Cacao farming remains one of the principal sources of income for farmers in areas such as West Africa and Central America. The processing and manufacturing of chocolate products create employment and add to the economies of countries like Belgium, Switzerland, and the United States.
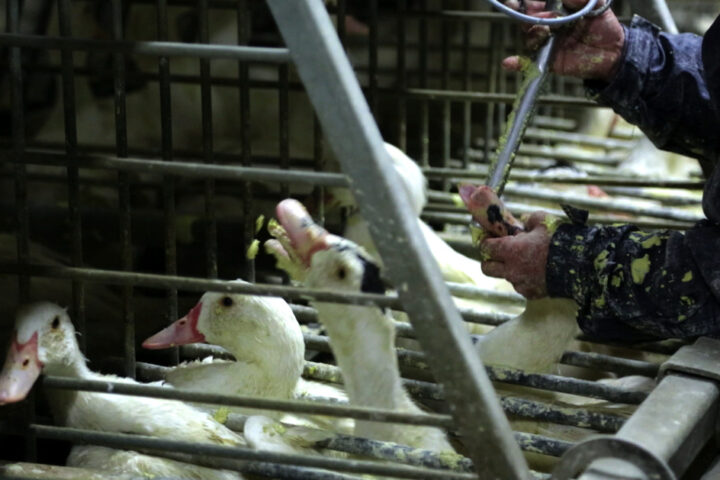
Child Labor in Cocoa Production
However, the most critical issue that the chocolate industry faces involves the employment of children. Children from as young as five are employed to work on plantations in many cocoa-producing countries. The children experience some rigorous conditions, such as long hours, physical labor, and exposure to harmful chemicals.
Child labor not only took away the childhood and education of children but also their health, since children will be at risk of serious injuries, malnutrition, and stunted growth. Child labor perpetuates cycles of poverty, as it keeps children trapped in their circumstances.
Deforestation and Habitat Loss
Its cultivation causes extreme impacts on the environment. Much habitat destruction and biodiversity loss is caused by the process of deforestation that has occurred along with the creation of cocoa plantations. Forests are responsible for managing climate change, for absorbing carbon dioxide, and for housing many species.
Furthermore, the destruction of forests leads to erosion, water pollution, and loss of valuable ecosystem services. Floods and droughts, among other dramatic natural disasters, result from deforestation.
Climate Change and Cocoa Production
Climate change threatens cocoa production on a significant scale. Thermo statistics, altered rainfall patterns, and increased instances of extreme weather events may affect the cultivation of cocoa. Droughts, pests, and diseases can decrease the quality and quantity of cocoa.
The chocolate industry should adapt to challenges regarding climate change, for example by developing and using climate-resilient cocoa varieties, sustainable farming practices, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Ethical sourcing and fair trade are critical issues in the sense that farming and production procedures need to be held ethical and fair in which farming communities especially benefit from cocoa and chocolate.
Ethical sourcing and fair trade practice meets the needs of many consumers and companies in solving the ethical and environmental issues surrounding chocolate production. Ethical sourcing will ensure chocolates are produced respecting human rights, safety, and security, protecting the environment, and supporting livelihoods in cocoa farming.
Fair trade certification also ensures that more money is paid to cocoa farmers for their product, allowing them to lift their living standards and contribute to better community development. Fair trade also promotes sustainable farming and social and environmental initiatives.
Consumer and Company Involvement
A great transformation in the chocolate industry largely depends on its consumers. Consumers choosing high-quality cocoa that is bought ethically and traded fairly are contributing to sustainable practices, improving peoples’ lives-even small-holder cocoa farmers.
Companies also have a role to play in being pro of ethically sourced chocolate. This they can achieve by coming up with fair sourcing policies, auditing their supply chains, and supporting initiatives for sustainable cocoa production.
Future of Chocolate: Sustainable and Ethical Industry
The future of chocolate rests highly on how the industry responds to these ethical and environmental challenges and manages them. Thus, such an industry would be a more sustainable and ethical force for good if it were able to promote sustainable practices while supporting initiatives of fair trade and even investing in research and development.
Being consumers who influence the future of chocolate, we can play a great part in this regard. From informed choices toward demanding ethical products, it will eventually help in creating a more sustainable and equitable chocolate industry.
Sources: