Source: Image by Deviantart_art- Elk-Cloner-Error-119507358
Introduction
The concept of a computer virus-a type of malware program that replicates itself and then spreads to other computers-is now an omnipresent one in our digital lifestyle. But where did that come from? How did the very first computer virus come into being? The answer lies in the early 1980s when a young programmer by the name of Richard Skrenta created a chunk of code that would forever change the landscape of computing: the Elk Cloner virus.
The Early Days of Computing
In the early 1980s, personal computers represented a relatively new and exciting technology. The Apple II, because it was gaining in popularity, became the home computer of choice for applications involving personal and business use. With growing numbers of users of Apple II, this created an increasing demand to share and exchange software. Therefore, it led to the promotion of floppy disk development, which then became the primary distribution media for software.
The Birth of Elk Cloner
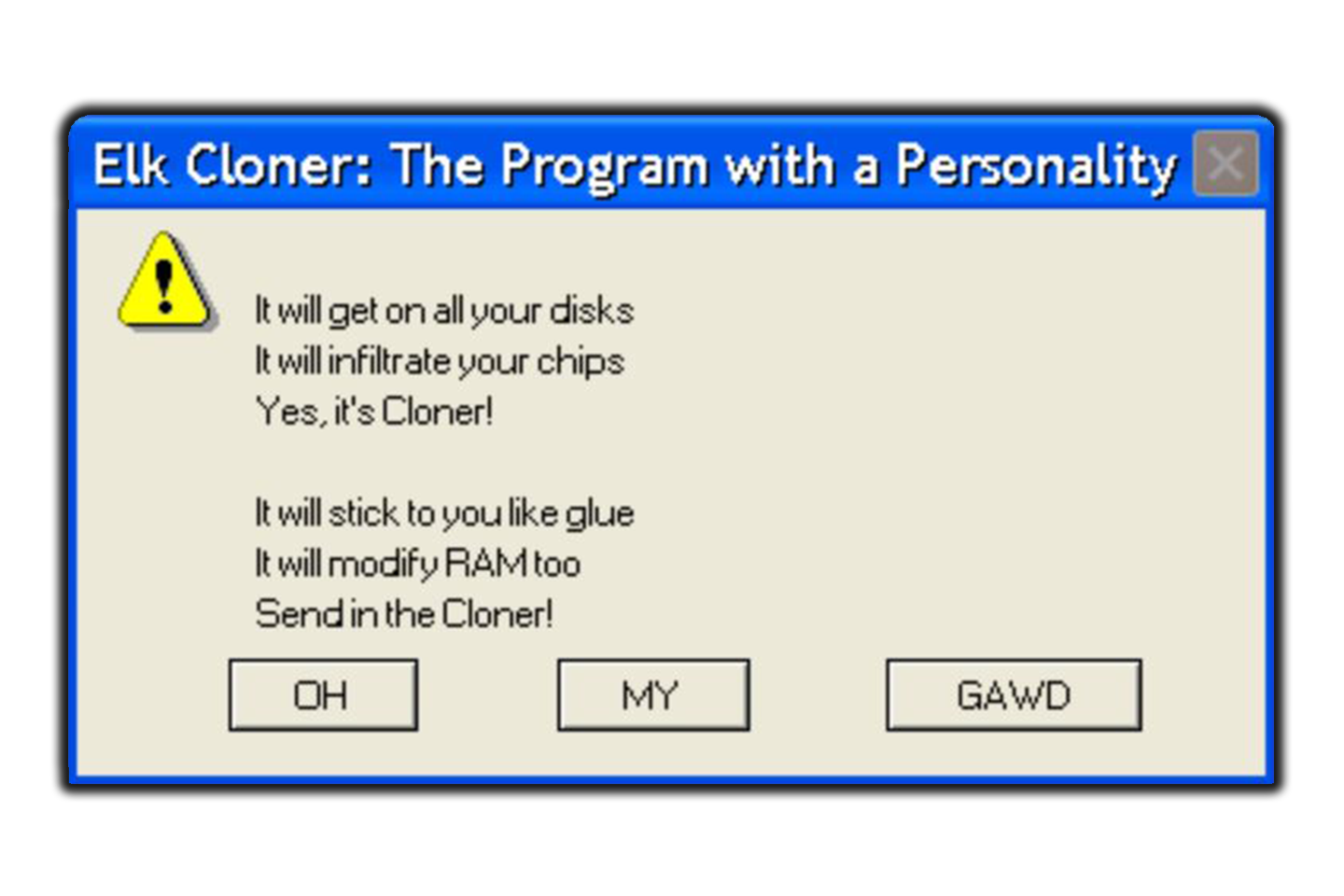
Richard Skrenta was an Apple II user and a teenager who lived in Pennsylvania. He was a few-year Balot.hstack programmer who loved furthering computers. In 1982, he decided that he wanted to create a prank program that would eventually infect the other Apple II computers. He managed to call this Elk Cloner; it would replicate onto other computers via floppy disks.
It was comparatively a simple program but for that time quite a breakthrough, as it was the first self-replicating computer virus and showed how such malware could spread and cause wide damages. While Elk Cloner was more or less an innocent prank, it paved the way to its more dangerous successors.
Elk Cloner Effects
The impact of Elk Cloner was far-reaching. It brought to the fore one key issue: computer security. It has raised awareness about malicious software. It also developed antivirus software, which is now an essential tool for protecting computers from viruses and other threats.
Besides computer security, Elk Cloner achieved several cultural missions. The virus became symbolic of the early days of computing and the spirit of experimentation and innovation typical for that time. The jolly tune, which played each time the virus infected a computer, was enlisted in a number of popular memes. Even the echo of this melody appeared in one documentary about the history of computing.
Computer Virus Evolution
It was only the beginning, as Elk Cloner was followed by other computer viruses in succeeding years, which were even more sophisticated and dangerous. There were new types of viruses that attack the boot sector of a computer’s hard drive, viruses that infect program files, and then there is the macro virus. Even these could cause considerable damage to computers and networks, deleting files and corrupting data; in some cases, disabling entire systems.
Along with the development of computer technology, new technologies of computer virus spreading emerged. Of course, emails rapidly became an easy way to spread viruses, and the internet was eventually used as a kind of worldwide network where viruses could spread. Nowadays, most types of viruses propagate via malicious websites, phishing attacks, and socially engineered methods.
Anti-Computer Viruses
The war against computer viruses is never won; new technologies continue to be developed by antivirus software companies for the detection and removal of viruses. Security researchers are finding new threats and developing countermeasures all the time. Governments and corporations have also installed measures in the way of network security protocols and incident response plans against cyber-attacks.
These efforts notwithstanding, the computer virus threat is still not at bay. New viruses are created on a daily basis, and quite often, it is hard to keep up with the newest threats. As our dependency on technology grows further, the awareness of risks and protection for ourselves and our data are quite necessary.
Network Viruses on the Rise
With the popularization of computer networks in the 1990s, computer viruses turned to exploiting this new interconnectedness of computers. Network viruses like the worm Code Red spread across the Internet in a matter of hours, infecting thousands of computers. Most of those viruses exploited either web servers or operating systems vulnerabilities for replication and propagating to other computers.
The Emergence of Polymorphic and Metamorphic Viruses
To elude detection, virus writers developed polymorphic and metamorphic viruses. These were viruses that, with every new infection, would look different to evade signature detection by the antivirus software. The Metamorphic viruses rewrite themselves completely as different code hence, very hard for the antivirus programs to find. Moreover,
The Era of Macro Viruses
The late 1990s saw the birth of a new kind of threat – the macro viruses. These resided within the Microsoft Office documents and had the capability to run malicious code when opened. The Melissa and Love Letter variants of the macro viruses were propagating through email, thus most energetically disrupting business and organizations throughout the world.
Internet Worm Era
The early 2000s brought about an era of worms, which spread through the Internet by exploiting certain vulnerabilities in network protocols. Important examples of worms that brought about large-scale damage are Nimda and Blaster. These worms disrupted network services and caused sensitive data to leak out.
The Age of Ransomware
In the last few years, ransomware has turned out to be one of the major cyber perils. Ransomware includes a class of malware that encrypts a target host’s files and renders them unusable, hence an eventual ransom from the victim can unlock his files. In recent times, these ransomware attacks have become so effectively sophisticated in order to attack businesses and people.
The Impact of Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks, including phishing and spear phishing, are also rampant in malware spreading. They deceive the victim into clicking a malicious link or opening an attachment with a virus or some other kind of malware.
The Rise of Mobile Malware
However, the increasing trend of smartphones and tablets called for a new kind of threat: mobile malware. Mobile malware, including both viruses and Trojans, can strike through malicious apps, compromised app stores, or through text message links to infected devices. Mobile malware can steal information from the victim, intercept the communication, and even result in taking control over the infected device.
The Role of Cybercrime Organizations
These are quite significantly leading roles that cybercrime organizations have played in the development and distribution of malware. Most of the organizations operate on an international scale using advanced techniques to avoid detection while making money from their illegal activities.
The Future of Malware
Malware menace evolves every day. The threats are endless and come one after another. With the improvement of technology, malware proliferation and methods of utilization will continue to improve as well. The individual and organizations need to remain updated on recent threats and take proper measures toward anti-cyber-attacks.
Conclusion
The origin of computer viruses was long and convoluted, extending through decades and reaching out to touch a wide range of malware. From the early times of the Elk Cloner to today’s sophisticated ransomware attacks, computer viruses kept evolving to adapt to new technologies. Considering the fast-growing dependency on technology, it is of vital importance to be aware of the risks and proactively take measures that will protect not just ourselves but our data as well.
Sources: