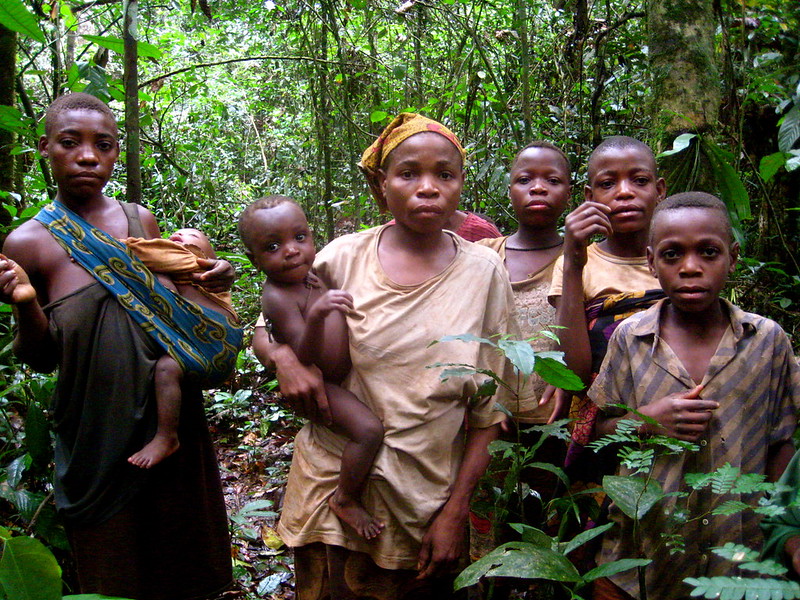
Source: Flickr_Baka Pygmies_Corinne Staley
Introduction
The Baka people, sometimes referred to as Pygmies, are a tribe of indigenous people who live deep within the rainforests of Central Africa. Their lives are completely interwoven with the forest, which is their home and source of nutrition. The richness of their relation with nature is highlighted, along with the profiled way of life that the Baka people have in relation to understanding biodiversity and living sustainably.
A Nomadic Lifestyle
The Baka are nomads, journeying into the forest for their subsistence needs. Their camps are temporary and flimsy, consisting of a few sticks and leaves, while they migrate according to the seasons. A nomadic lifestyle allows them to benefit from all types of fruits and nuts and other products of the same area without the area being destroyed.
Hunting and Gathering: A Way of Life
Hunting and gathering are the Baka’s primary sources of subsistence. They hunt monkeys, antelopes, and small game with their classic techniques, using bows and arrows, spears, and snares. Their knowledge of the forest is unmatched: with no problems, they are able to spot edible plants against a highly complex background or track animals and make one’s way with ease through thick undergrowth.
Music and Dance: A Cultural Tapestry
Music and dance are the important aspects of Baka culture. Their musical talent reflects in the complicated rhythms with harmonious vocals. Traditional performances are always accompanied by different instruments, including drums, xylophones, and flutes. Music and dance are a means of communicating, storytelling, and maintaining social bonds.
Oral Traditions: Ways of Passing Knowledge
The Bakas have a rich oral tradition, whereby the stories, various myths, and legends are passed down from generation to generation. These stories very often tell of the forest and its dwellers and of the Baka’s relations with nature. Through oral storytelling, the passing of knowledge and culture is deeply inculcated in the people. Spiritual Connection to Nature
The Baka people are spiritually attached to the forest. They believe in ancestral spirits and gods of nature that are believed to reside among the trees, rivers, and animals. It is this spiritual connection that guides their interaction with the environment and shapes their perception of the world.
Challenges Faced by the Baka

Wikimedia_Pygmées_(RDC)By Élie Nzuzi – Own work CC BY-SA 4.0
Inspite of their close relation with the forest, Bakas are beset with so many challenges. Definitely, outside invasion brings encroachment, logging, and deforestation, due to which habitat loss is taking place, threatening the very existence of the Baka community by displacing them, and therefore erosion of their culture as well.
Protection Efforts for Baka and Their Ecology
Over the recent years, there are those who have worked towards protection of the Baka and their environment. Many organizations and individuals work in trying to create awareness about their plight and advocate for recognition of their rights. In addition, various sustainable development projects have aimed at conserving the rainforest with the view to sustain the livelihoods of the Baka people.
The Contribution of Baka to Biodiversity Conservation
The Baka are a significant source of knowledge about the forest for biodiversity conservation. Their traditional practices, in many ways, help in the preservation of ecosystems and the protection of endangered species. By being able to understand the relationship that they have with the forest, scientists and conservationists can learn how to take care of it effectively. The
Role of Baka in Climate Change Mitigation
The fact that the traditional knowledge of the Baka has extensive implications for climate change mitigation means that deep knowledge of the forest and sustainable use of its resources may contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and protecting carbon sinks.
Traditional Forest Management Practices
Centuries of interaction with the environment have led the Baka to develop sustainable forest management that includes no clear-cutting and insufficient hunting to keep the forest healthy and resistant. Their knowledge of plant ecology allows them to identify and conserve all those tree species that are really fundamental for carbon sequestration.
Agroforestry and Biodiversity Conservation
Agroforestry is often practiced among the Baka whereby trees are integrated with crops in the agricultural systems. This concept therefore enhances the promotion of forest cover, soil fertility, and biodiversity. In promoting the biodiversity within the forest, the Baka enhances the resilience of the ecosystem by its ability to sequester carbon.
Traditional Knowledge and Adaptation to Climate Change
The traditional knowledge of the Baka is extremely valuable in terms of gauging climate change adaptation. Over generations, they have witnessed the changes in the environment of the forest and have developed ways to adapt to these changes. Their traditional knowledge regarding local weather trends, plant phenology, and animal behavior can be useful for adapting to climate change.
Challenges and Opportunities
Their contribution to the reduction of climate change is very important, though the Baka are highly affected by deforestation, logging, and land encroachment, both of which threaten their way of life and the integrity of the rainforest. It is for this reason that there are opportunities available that create ways of supporting the Baka in sustainable development efforts.
Community-Based Conservation Initiatives
Community-based conservation can empower them and recognize the Baka as protectors of the forest. This may involve protection areas, livelihood development, and cultural heritage. In partnership with the Baka, conservation organizations have the ability to use traditional knowledge and skills in the protection of the rainforest and Climate Change.
Indigenous Rights are Important
For the Baka’s protection, it is very important that they contribute a great deal to mitigating climate change. Their land and cultural rights should be recognized to give them an option in the disposition and management of the forest. We will support their struggle to protect the rainforest in recognition of their rights and in contribution to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
The Baka are very important companions in the fight against climate change. Their traditional knowledge, their sustainable way of life, and the strong bond they have with the forest give meaning and a solution to many questions. Supporting the Baka and their communities will offer protection for the rainforest, mitigate climate change, and support a more equitable and sustainable future for all humankind.
Sources:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Baka_people_(Cameroon_and_Gabon)#:~:text=Baka%20people%20are%20all%20hunter,against%20and%20marginalized%20from%20society.
- https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/nov/26/you-have-stolen-our-forest-rights-of-baka-people-in-the-congo-ignored
- https://www.theguardian.com/global-development/2016/may/04/life-for-the-baka-pygmies-of-central-african-republic
- https://kanseisounds.com/kanseisounds/baka-guardians-forest/